Introduction
The IEEE RAS Technical Committee on Digital Manufacturing and Human-Centered Automation (RAS TC) was approved and established during the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) in Brisbane, Australia, 21-26 May 2018.
This RAS TC serves as reference forum to promote research, development and innovation under two constitutive sub-fields:

Digital Manufacturing- Embraces and represents the principles of total connection in the factory, integrating automation of production, stock management, product orders and labor force management.

Bio-Automation- Sustainable production, co-robotics, circular economy, design for disassembly and waste management, oriented to eco-green social responsibility that can be termed as Bio-Automation. The term Bio-Automation includes Human-Centered and environmentally friendly automation.
What do we mean by the term “Human-Centered automation”? It is the synergistic interaction between extreme optimization of processes targeted by Digital Manufacturing and the social responsibility of Bio-Automation.
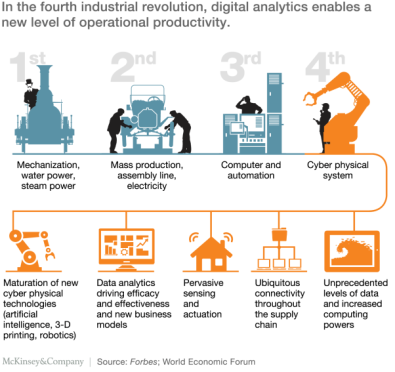
The IC3 (Collaborative, Connected and Cognitive) paradigm has been heralding a fundamental positive impact on global economy, with both Automation and Artificial Intelligence driving the fourth industrial revolution. In the fourth industrial revolution, digital analytics enables a new level of operational productivity.


The emerging generation of collborative robots will become humans’ work-mates, instead of competitive replacements, and will play a key role in reshaping the quantity and quality of jobs. Collaborative robots, well integrated in manufacturing industries, co-operate/assist the worker in a bioinspired way, promoting safety at work and improving the eco-sustainability of industrial processes.
Scope
Among the main objectives of the TC there are:
- to address the emerging field of anthropocentric robotic systems for Automation, leveraging on sustainability in several respects: socially, ethically, energetically and ecologically; and on biomechanical studies to characterize and reverse-engineer worker’s gestures and to evaluate the stress suffered by their musculoskeletal system;
- to guide academic and entrepreneurial/industrial communities towards the procurement and the integration of disruptive (such as collaborative robots, digital manufacturing, 3-D printing, industrial IoT/cyberphysical systems and Clouds,…,) safely and smoothly complemented with humans within manufacturing processes;
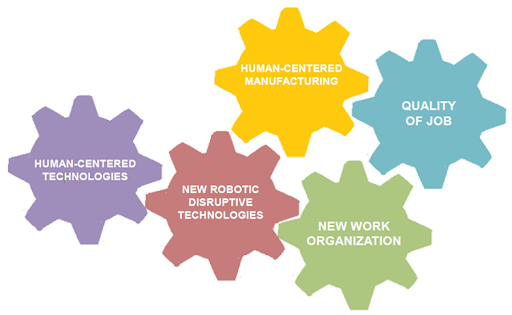
- to address crucial challenges such as the ethical issues on the future role of humans and Automation and the effect of the introduction of these disruptive robotic technologies on working conditions, quality of job, work organization;
- to re-shape production processes;
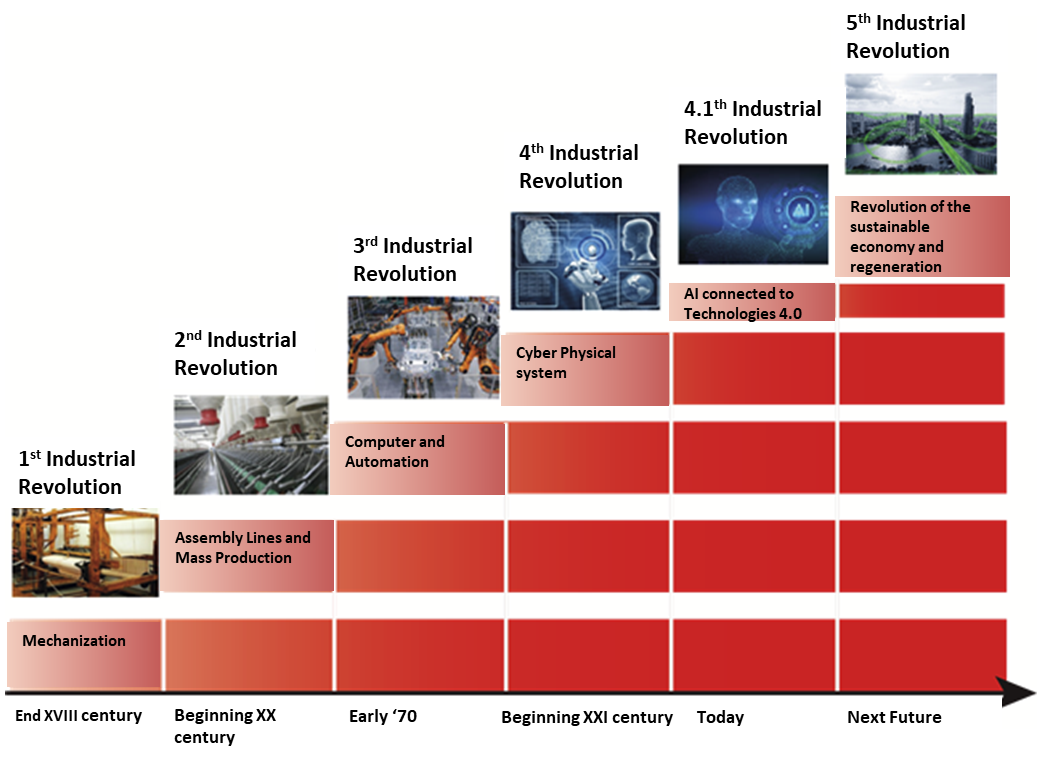
- to be active in the Fifth Industrial Revolution.
Impact
The expected impact is to increase efficiency and competitiveness of industrial processes, through the use of interconnected and collaborative robots. Collaborative robots in the manufacturing industries co-operate/assist the worker in a bioinspired way, promoting safety at work and improving the eco-sustainability of industrial processes.
The adoption of these new technologies will lead to a reallocation of tasks from humans to machines: the first will devote themselves to cognitive tasks and coordination/problem solving activities whereas machine will take care of the routinized ones.
Goals
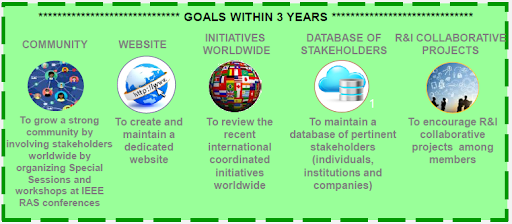
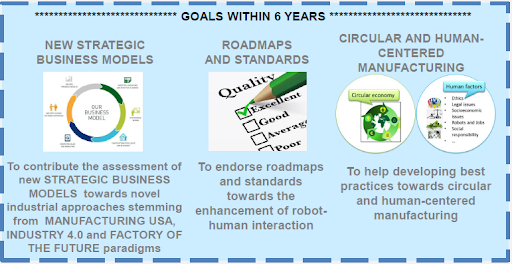
Topics of interest
Priority areas for this RAS TC are:
- key scientific and technical problems related to Smart Factories and novel approaches to robotics and automation;
- synergistic interaction between extreme optimization of industrial processes, targeted by Digital Manufacturing, and the social responsibility of Human-Centered Automation;
- future transformations of manufacturing and its impact on R&D and innovation challenges;
- challenges and benefits of networked robots and industrial IT;
- eco-sustainability of industrial processes;
- recycling production processes of waste materials;
- anthropocentric robotic systems for Automation;
- safe and intuitive interaction with workers and enhanced human-machine co-operation;
- real cases on efficient and competitive sustainable processes, through the development of interconnected and collaborative robots integrated in manufacturing processes.
- Consumer Robots, Industrial Robots, Service Robots;
- Wearable robots (exoskeletons) to ease domestic tasks;
- Precision, accuracy and repeatability in Robotics;
- Safety and efficient processes to reduce human hazard and the risk of human error;
- Multi-modal interfaces and human-robot interaction;
- Robotics and AI;
- Robotics in Automation;
- Collaborative Robotics;
- Distributed and Cloud Robotics.
Membership
If you are interested in becoming a member of this committee, please fill out the form.
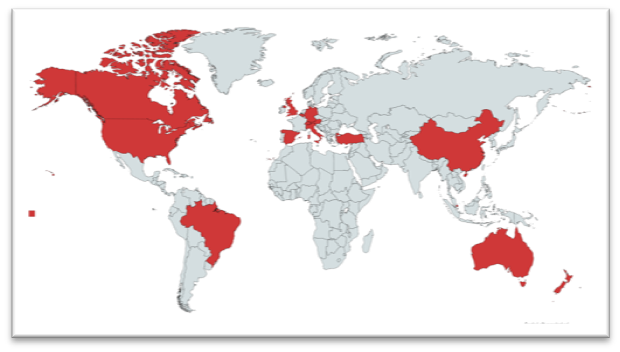
Geographic distribution of our members: